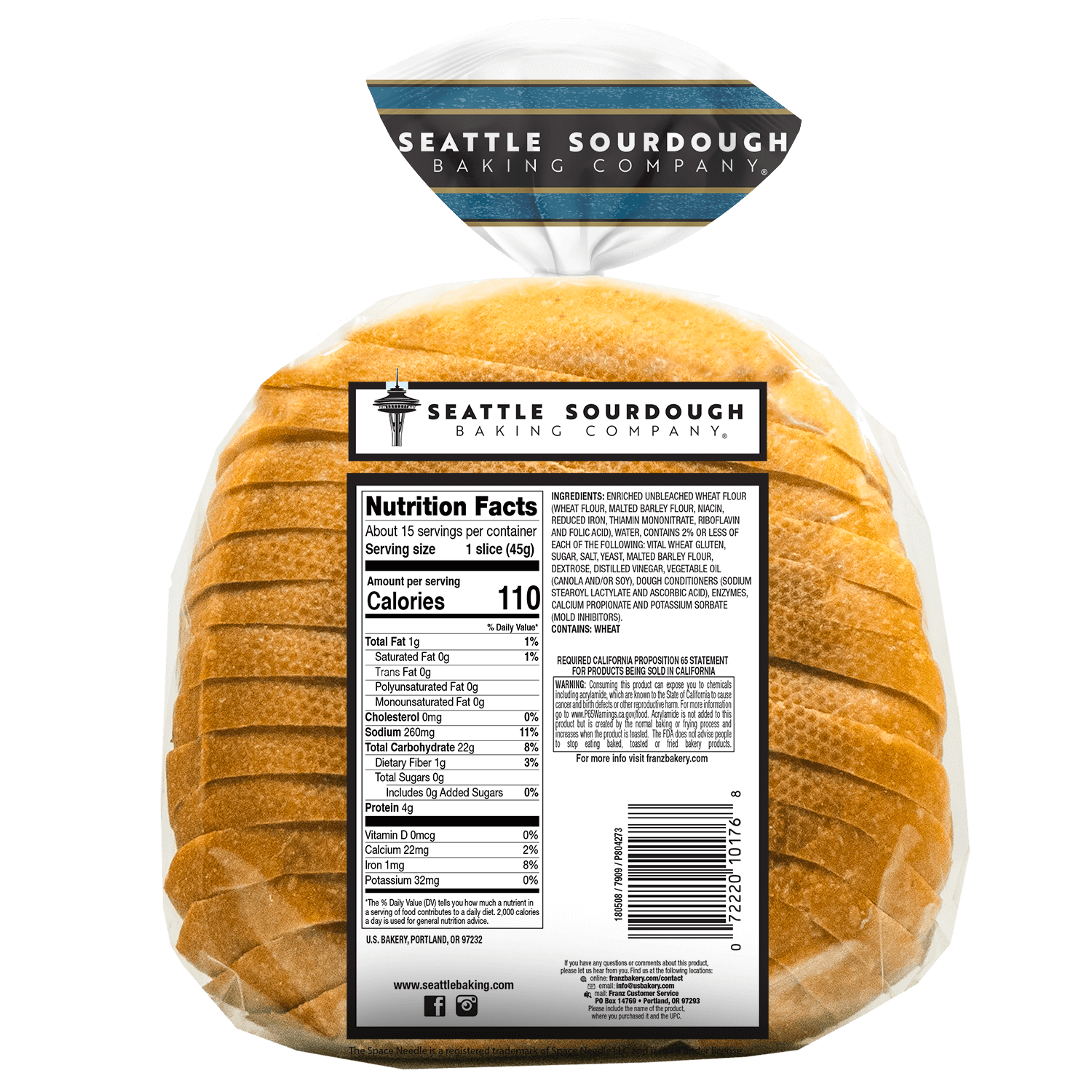
When it comes to daily nutrition, bread is often a staple in many households worldwide. But have you ever wondered about the nutrition in bread slice? What exactly does it offer, and how does it fit into a balanced diet? From providing essential carbohydrates to offering surprising amounts of fiber and micronutrients, bread slices can be more than just a base for your sandwiches. Whether you're munching on whole grain, multigrain, or white bread, understanding its nutritional profile can help you make informed dietary choices. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of bread slices, exploring their nutritional value, health benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Bread has been a dietary cornerstone for centuries, evolving from simple flatbreads to the diverse range of loaves we see today. Each slice carries a unique blend of nutrients, depending on its type and ingredients. While some bread varieties are fortified with vitamins and minerals, others rely on natural components like whole grains and seeds to provide nutritional value. By examining the ingredients and preparation methods, we can better understand how bread contributes to our overall health. This article will guide you through everything you need to know about the nutrition in bread slice, ensuring you can enjoy it guilt-free while maximizing its benefits.
As we explore the topic further, you’ll discover how bread fits into modern dietary trends, including gluten-free and low-carb lifestyles. We’ll also address common misconceptions about bread and its nutritional content. Whether you’re a health enthusiast or simply curious about the food you consume, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make smarter choices. So, let’s unravel the nutritional secrets hidden in every slice of bread and learn how it can enhance your diet without compromising your health goals.
Read also:Unveiling The Mysteries Of The 1974 Chinese Zodiac Insights And Guidance
Table of Contents
- What Makes Bread Nutritious?
- How Does Bread Contribute to Daily Nutrition?
- Is Bread a Healthy Choice for Everyone?
- Types of Bread and Their Nutritional Differences
- How Can You Choose the Healthiest Bread?
- What Are the Potential Drawbacks of Bread Consumption?
- How Does Bread Fit Into Special Diets?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Nutrition in Bread Slice
What Makes Bread Nutritious?
Bread is more than just a source of carbohydrates; it can be a powerhouse of essential nutrients depending on its composition. The primary ingredients in bread—flour, water, yeast, and salt—form the foundation of its nutritional profile. However, modern bread-making often includes additional components like whole grains, seeds, and fortifications that enhance its health benefits. Let’s explore what makes bread a nutritious addition to your diet.
The Role of Whole Grains
Whole grain bread is a standout when it comes to nutrition in bread slice. Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain all parts of the grain kernel—the bran, germ, and endosperm. This means they are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Fiber, in particular, plays a crucial role in digestive health, helping to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. Additionally, whole grains are linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Fiber: Promotes digestive health and keeps you feeling full longer.
- Vitamins: Whole grains are a good source of B vitamins, which support energy metabolism.
- Minerals: Contains essential minerals like magnesium, iron, and zinc.
Fortified Bread and Its Benefits
Many bread varieties are fortified with additional nutrients to address common dietary deficiencies. For instance, bread is often enriched with folic acid, a B vitamin that is crucial for pregnant women to prevent neural tube defects in developing fetuses. Fortified bread may also include iron, calcium, and vitamin D, making it a convenient way to boost your daily nutrient intake. This fortification process ensures that even white bread, which is typically lower in nutrients, can contribute positively to your diet.
How Does Bread Contribute to Daily Nutrition?
Bread is a versatile food that can provide a significant portion of your daily nutritional needs. From carbohydrates for energy to essential vitamins and minerals, bread plays a vital role in maintaining a balanced diet. Let’s break down how bread contributes to your daily nutrition and why it’s a staple for many.
Carbohydrates: The Energy Powerhouse
Carbohydrates are the primary macronutrient found in bread, making it an excellent source of energy. Each slice of bread contains around 15-20 grams of carbohydrates, depending on the type. These carbs are broken down into glucose, which fuels your brain and muscles. For individuals with active lifestyles, bread can be an efficient way to replenish energy stores after physical activity.
Protein and Amino Acids
While bread is not typically known for its protein content, certain varieties, like whole grain or seeded bread, contain modest amounts of protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, and bread can contribute to your daily protein intake, especially when paired with other protein-rich foods like cheese, eggs, or nut butter.
Read also:Discovering Lily Cates Biography Career And Influence
Pairing Bread for Maximum Nutrition
To maximize the nutritional benefits of bread, consider pairing it with nutrient-dense toppings. For example:
- Avocado: Adds healthy fats and fiber.
- Eggs: Boost protein and essential vitamins.
- Nut Butter: Provides healthy fats and additional protein.
Is Bread a Healthy Choice for Everyone?
While bread can be a nutritious addition to many diets, it may not be suitable for everyone. Factors such as dietary restrictions, allergies, and health conditions can influence whether bread is a healthy choice for an individual. Let’s explore this question in detail.
Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease
For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, traditional bread made from wheat, barley, or rye can cause adverse reactions. Symptoms may include bloating, diarrhea, fatigue, and even nutrient malabsorption. Fortunately, gluten-free bread options made from rice flour, almond flour, or other alternatives are widely available, allowing those with gluten intolerance to enjoy bread safely.
Low-Carb and Keto Diets
People following low-carb or ketogenic diets often avoid bread due to its high carbohydrate content. However, low-carb bread alternatives, such as those made from almond flour or coconut flour, provide a solution. These breads are lower in carbs and higher in fat, aligning with the macronutrient requirements of these diets.
Types of Bread and Their Nutritional Differences
Not all bread is created equal. The nutritional content of bread varies significantly depending on its type and ingredients. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best option for your dietary needs.
Whole Grain vs. White Bread
Whole grain bread is generally more nutritious than white bread due to its higher fiber and nutrient content. White bread, on the other hand, is made from refined flour, which strips away much of the grain’s natural goodness. While white bread is often fortified with vitamins and minerals, it lacks the fiber and complex carbohydrates found in whole grain varieties.
Comparing Nutritional Profiles
| Type of Bread | Calories per Slice | Fiber (g) | Protein (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Grain | 80 | 3 | 4 |
| White Bread | 70 | 1 | 2 |
How Can You Choose the Healthiest Bread?
With so many bread options available, choosing the healthiest one can be overwhelming. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision.
Check the Ingredients List
The first ingredient on the label should ideally be whole grain or whole wheat flour. Avoid breads that list enriched flour as the primary ingredient, as this indicates refined grains. Additionally, look for breads with minimal added sugars and artificial preservatives.
Opt for Fortified Varieties
Fortified bread can provide additional nutrients like folic acid, iron, and vitamin D. These enhancements make bread a convenient way to meet your daily nutritional requirements.
What Are the Potential Drawbacks of Bread Consumption?
While bread can be nutritious, it’s important to be aware of its potential drawbacks. Overconsumption of certain types of bread, particularly white bread, can lead to weight gain and blood sugar spikes due to its high glycemic index.
Portion Control is Key
Enjoying bread in moderation is essential to avoid excessive calorie intake. Pairing bread with protein-rich or fiber-rich foods can help mitigate blood sugar spikes and promote satiety.
How Does Bread Fit Into Special Diets?
Bread can be adapted to fit various dietary preferences, from vegan to gluten-free. Understanding how to incorporate bread into these diets ensures you don’t miss out on its nutritional benefits.
Vegan-Friendly Bread Options
Most bread is naturally vegan, but it’s important to check for hidden animal-derived ingredients like milk or honey. Opt for bread labeled as vegan to ensure compliance with your dietary choices.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nutrition in Bread Slice
Is Bread High in Calories?
On average, a single slice of bread contains 70-100 calories, depending on its type. Whole grain bread tends to be slightly higher in calories due to its denser composition.
Can Bread Help with Weight Loss?
Yes, bread can support weight loss when consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-dense foods. Whole grain bread, in particular, promotes satiety and reduces cravings.
Does Bread Cause Bloating?
Bloating can occur in individuals sensitive to gluten or certain carbohydrates found in bread. Opting for gluten-free or low-FODMAP bread may alleviate these symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the nutrition in bread slice is a multifaceted topic that depends on the type of bread and its ingredients. By understanding its nutritional profile and making informed choices, you can enjoy bread as part of a balanced diet. Whether you’re seeking energy, fiber, or essential vitamins, bread can be a valuable addition to your meals.
For more information on healthy eating, check out this resource on nutrition.
/bread-crop-23e1fc54583d435d938ee31bbe66779e.jpg)