When it comes to electrical systems, safety and efficiency are paramount. One of the most critical decisions homeowners and electricians face is selecting the correct wire size for 150 amp service. This choice impacts the performance of your electrical system, ensuring it can handle the load without overheating or causing hazards. A 150 amp service is commonly used in modern homes, especially those with high energy demands due to appliances like air conditioners, electric heaters, and large kitchen equipment. Choosing the wrong wire size can lead to inefficiencies, frequent circuit breaker trips, or even electrical fires. Therefore, understanding the nuances of wire sizing is essential for a reliable and safe electrical setup.
Electrical codes and standards exist for a reason: to protect both property and people. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for wire sizes based on amperage, distance, and material type. For a 150 amp service, these guidelines are particularly important because the wires must carry a significant amount of current without excessive voltage drop. Voltage drop occurs when the electrical resistance in the wire causes a reduction in voltage as electricity travels from the source to the load. This can lead to underperformance of appliances and equipment, making it crucial to adhere to recommended wire sizes.
Beyond safety and performance, selecting the right wire size for 150 amp service also has financial implications. Undersized wires can lead to increased energy losses, higher electricity bills, and potential damage to expensive appliances. On the other hand, oversized wires may unnecessarily increase material costs. Striking the right balance requires a thorough understanding of factors such as wire material (copper or aluminum), insulation type, and the specific demands of your electrical system. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about wire size for 150 amp service, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Read also:Jaden Smith P Diddy Unveiling Their Influence Legacy And Impact
Table of Contents
- What Is the Best Wire Size for 150 Amp Service?
- Why Does Wire Size Matter for 150 Amp Service?
- How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Wire Size?
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Material is Best for 150 Amp Service?
- What Are the National Electrical Code Guidelines for 150 Amp Service?
- How to Choose the Right Insulation Type for 150 Amp Service?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size for 150 Amp Service
- Frequently Asked Questions About Wire Size for 150 Amp Service
What Is the Best Wire Size for 150 Amp Service?
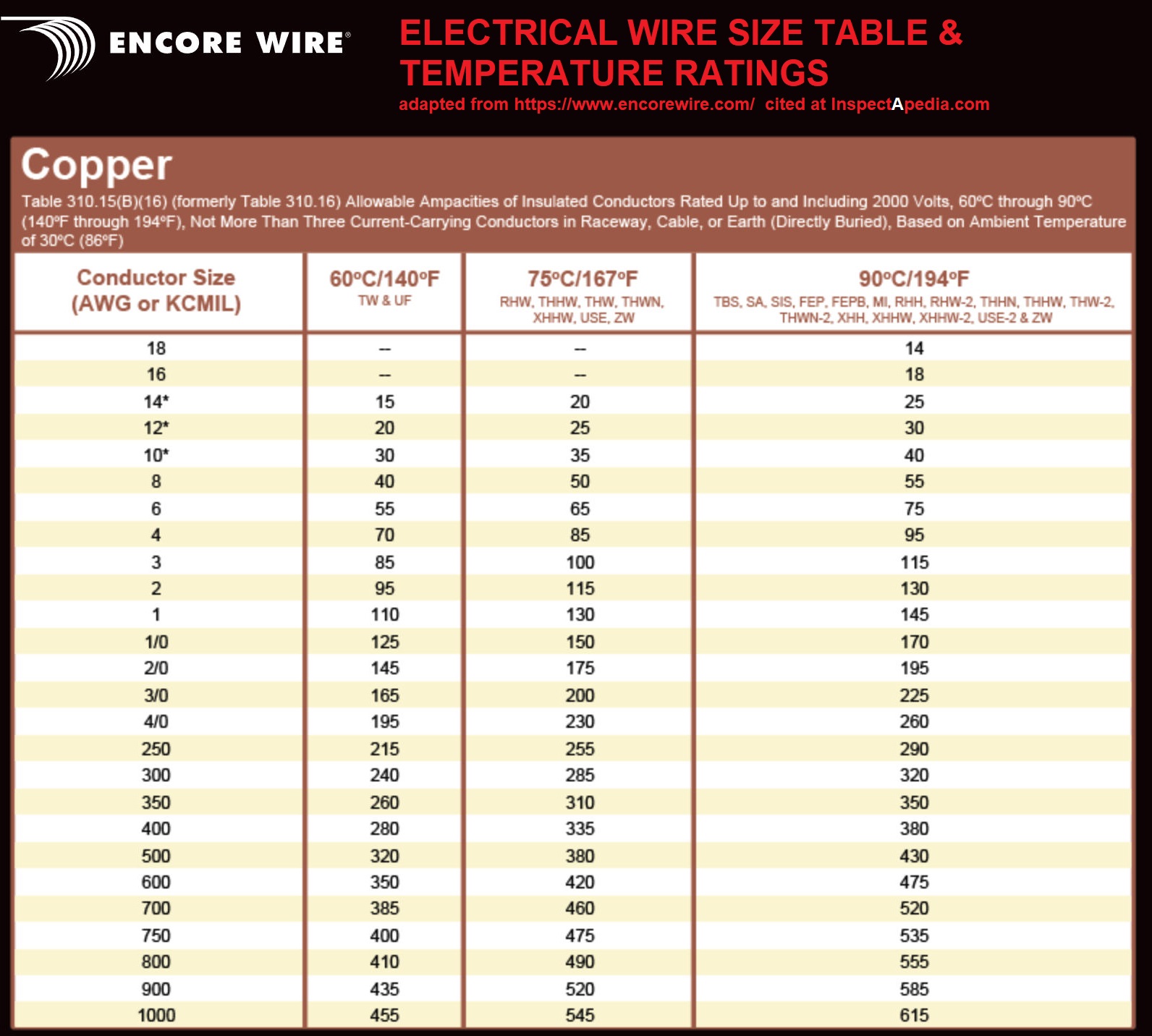
Choosing the correct wire size for 150 amp service depends on several factors, including the type of wire material, the distance from the electrical panel to the load, and the insulation rating. For most residential applications, a 150 amp service typically requires either a 1/0 AWG copper wire or a 2/0 AWG aluminum wire. These sizes are designed to handle the current load safely while minimizing voltage drop.
Copper wires are generally preferred for their superior conductivity and durability. A 1/0 AWG copper wire has a diameter that allows it to carry up to 150 amps over short distances without significant voltage loss. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum, which is why many homeowners opt for aluminum wires when cost is a concern. Aluminum wires, while less conductive, are lighter and more affordable, making them a practical choice for larger installations.
When selecting wire size, it’s also important to consider the insulation type. For example, THHN/THWN-2 insulation is commonly used for 150 amp services because it is heat-resistant and suitable for both dry and wet locations. This ensures that the wire can withstand varying environmental conditions without degrading. Additionally, using wires with higher temperature ratings (e.g., 90°C) can provide extra safety margins, especially in areas with high ambient temperatures.
Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection
Several factors influence the choice of wire size for 150 amp service:
- Distance: Longer runs require larger wire sizes to compensate for voltage drop.
- Material: Copper offers better conductivity but is more expensive than aluminum.
- Insulation Rating: Higher temperature ratings provide better performance in extreme conditions.
Common Wire Sizes for 150 Amp Service
- 1/0 AWG Copper
- 2/0 AWG Aluminum
Why Does Wire Size Matter for 150 Amp Service?
The wire size you choose for a 150 amp service directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. Undersized wires can lead to overheating, which poses a significant fire hazard. When a wire is too small to handle the current load, it generates excessive heat due to resistance. Over time, this heat can degrade the wire’s insulation, leading to exposed conductors and potential short circuits.
On the other hand, oversized wires, while safer, can be unnecessarily expensive and cumbersome to install. They may also require larger conduits and connectors, increasing the overall complexity of the installation process. Therefore, striking the right balance is crucial. Properly sized wires ensure that the electrical system operates within safe parameters, minimizing energy losses and maximizing performance.
Read also:Edward Ruttle A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Legacy And Achievements
Impact of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop is another critical factor influenced by wire size. When the voltage drops below acceptable levels, appliances and equipment may not function correctly. For example, motors may run slower, lights may dim, and sensitive electronics could malfunction. To mitigate voltage drop, it’s essential to use wires that can handle the current load over the specified distance without significant resistance.
How to Calculate Voltage Drop for Wire Size?
Calculating voltage drop is a straightforward process that involves a few key variables: wire size, material, distance, and current load. The formula for voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = (2 × Length × Current × Resistance) / 1000
Where:
- Length: The distance from the electrical panel to the load in feet.
- Current: The amperage of the circuit (150 amps in this case).
- Resistance: The resistance per 1,000 feet of the wire, which depends on the wire size and material.
For example, if you’re using a 1/0 AWG copper wire over a 100-foot distance, the resistance is approximately 0.1 ohms per 1,000 feet. Plugging these values into the formula gives:
Voltage Drop = (2 × 100 × 150 × 0.1) / 1000 = 3 volts
This result indicates a 3-volt drop, which is within acceptable limits for most applications. However, if the distance were longer, the voltage drop would increase, necessitating a larger wire size.
Tools for Voltage Drop Calculation
Several online calculators and mobile apps can simplify the voltage drop calculation process. These tools allow you to input the wire size, material, distance, and current load to determine whether the selected wire is suitable for your application.
Copper vs. Aluminum: Which Material is Best for 150 Amp Service?
When selecting wire material for a 150 amp service, the choice often comes down to copper or aluminum. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages, and the decision depends on factors such as budget, application, and installation requirements.
Copper is the preferred choice for many electricians due to its superior conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion. It can carry more current than aluminum of the same size, making it ideal for applications where space and weight are critical. However, copper is significantly more expensive, which can be a deterrent for large-scale installations.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter and more cost-effective. It is commonly used in residential and commercial applications where budget constraints are a concern. However, aluminum wires require special connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection. Additionally, aluminum has a higher resistance than copper, meaning larger wire sizes are needed to achieve the same performance.
Comparison of Copper and Aluminum Wires
| Material | Conductivity | Cost | Weight | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High | Expensive | Heavy | Excellent |
| Aluminum | Moderate | Affordable | Lightweight | Fair (requires maintenance) |
What Are the National Electrical Code Guidelines for 150 Amp Service?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides comprehensive guidelines for wire sizing to ensure safety and compliance. According to the NEC, the minimum wire size for a 150 amp service is 1/0 AWG for copper and 2/0 AWG for aluminum. These recommendations are based on the wire’s ability to handle the current load without exceeding a 3% voltage drop.
In addition to wire size, the NEC also specifies requirements for insulation, grounding, and conduit sizing. For example, all wires must be properly insulated to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits. Grounding is another critical aspect, as it provides a safe path for electrical current in the event of a fault.
Key NEC Requirements
- Minimum wire size: 1/0 AWG copper or 2/0 AWG aluminum.
- Insulation must meet temperature and environmental ratings.
- Grounding must comply with NEC standards.
How to Choose the Right Insulation Type for 150 Amp Service?
Insulation plays a vital role in protecting wires from environmental factors and ensuring safe operation. For a 150 amp service, common insulation types include THHN/THWN-2, XHHW, and USE. Each type has specific characteristics that make it suitable for different applications.
THHN/THWN-2 is widely used in residential and commercial wiring due to its heat resistance and versatility. It is rated for both dry and wet locations, making it ideal for a variety of environments. XHHW is another popular choice, particularly for underground installations, as it is designed to withstand moisture and extreme temperatures. USE (Underground Service Entrance) cables are specifically designed for direct burial applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insulation
- Environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, temperature).
- Application (e.g., indoor, outdoor, underground).
- Cost and availability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Wire Size for 150 Amp Service
Selecting the wrong wire size for a 150 amp service can have serious consequences. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Ignoring Voltage Drop: Failing to account for voltage drop can lead to underperforming appliances and equipment.